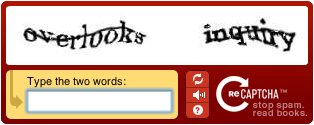
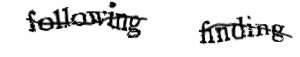A CAPTCHA is a program that protects websites against bots by generating and grading tests that humans can pass but current computer programs cannot. For example, humans can read distorted text as the one shown below, but current computer programs can't:
CAPTCHAs are used in attempts to prevent automated software from performing actions which degrade the quality of service of a given system, whether due to abuse or resource expenditure. CAPTCHAs can be deployed to protect systems vulnerable to e-mail spam, such as the webmail services of Gmail, Hotmail, and Yahoo! Mail.
CAPTCHAs are also used to minimize automated posting to blogs, forums and wikis, whether as a result of commercial promotion, or harassment and vandalism. CAPTCHAs also serve an important function in rate limiting. Automated usage of a service might be desirable until such usage is done to excess and to the detriment of human users. In such cases, administrators can use CAPTCHA to enforce automated usage policies based on given thresholds. The article rating systems used by many news web sites are another example of an online facility vulnerable to manipulation by automated software. As of 2010, most CAPTCHAs display distorted text that is difficult to read by character recognition software.

Because CAPTCHAs rely on visual perception, users unable to view a CAPTCHA due to a disability will be unable to perform the task protected by a CAPTCHA. Therefore, sites implementing CAPTCHAs may provide an audio version of the CAPTCHA in addition to the visual method. The official CAPTCHA site recommends providing an audio CAPTCHA for accessibility reasons, but it is not usable for deafblind people or for users of text web browsers.
Even audio and visual CAPTCHAs will require manual intervention for some users, such as those who have disabilities. There have been various attempts at creating more accessible CAPTCHAs, including the use of JavaScript, mathematical questions ("how much is 1+1") and common sense questions ("what colour is the sky on a clear day"). However, these types of CAPTCHAs do not meet the criteria for a successful CAPTCHA. They are not automatically generated and they do not present a new problem or test for each attack.
Some researchers promote image recognition CAPTCHAs as a possible alternative for text-based CAPTCHAs. Computer-based recognition algorithms require the extraction of color, texture, shape, or special point features, which cannot be correctly extracted after the designed distortions. However, human can still recognize the original concept depicted in the images even with these distortions.